
TAXATION
SERVICES
CPA Group Strengthens its Specialist Tax Team
CPA Group’s taxation services is divided into two (2) major services, namely, Investigation and Audit services, and Tax Compliance services. To enhance the quality of the services that is provided, CPA Group has put up a specialist team, consisting of qualified professionals working in tandem with retired senior IRB members.
Increased vigilance by IRB officials has made it imperative that our taxation team is armed with the required knowledge and connections, needed to achieve the desired outcome.
1. Introduction of Malaysia Tax System
Malaysia Tax System
The reason behind this arrangement is to instill the culture of voluntary compliance onto tax payers while reducing the workload of the IRB Department so that more time can be channeled to higher risk areas in order to avoid potentially significant loss of revenue.
A consequent of this system would be stricter IRB enforcement for non- tax compliances, with heavier penalty provisions for tax offenders.
2. Taxation Services
I. Tax Investigation and Audit
Tax Investigation
Investigation case may be selected using various methods such as:
- Risk analysis
- Information from informer
- Review of Income Tax Return
- Intelligence Information
- Information from other law information agencies
With effect from 1st January 2020, the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (LHDN) revised its official guideline, Tax Investigation Framework 2020, with the purpose of updating taxpayers on the latest tax investigation procedures.
Please refer to the table for the steps undertaken by IRB in their investigative exercise.
IRB’s Tax Investigation Procedures
| Step | Procedures | Explanatory |
| 1 | Request for documents and information | – An investigation can be carried out with the issuing of letters requesting for documents and information from the taxpayer, tax agents and third parties.
– The taxpayer may be required to give information along with an oral explanation at LHDN offices |
| Or
Inspection Visit |
– Investigations can also be carried out with an inspection visit without prior notice, to the taxpayer’s business premises, residences, tax agent’s premises, third parties and other premises as necessary. | |
| 2 | Examination
of Documents |
The LHDN officer will inspect the taxpayer’s business documents and/or personal documents.
– The inspection is to gather evidence of tax evasion and request any party to produce documents in his custody or control. |
| 3 | Recording of Statements | – At least two LHDN officers will be present during the recording of statements from persons related to the case being investigated.
– Qualified lawyers can be present during the recording of statements as well. |
| 4 | Finalisation of Investigation | i) After completion of the investigation procedures, LHDN will issue a letter to the taxpayer confirming the finalisation of the investigation
ii) If a settlement is agreed upon, an agreement or letter of undertaking will be signed.
iii) The investigation is considered finalised after the case is approved by the DG of LHDN and an assessment is raised. Taxpayers who have been investigated will be monitored by LHDN.
iv) If the taxpayer does not agree with the investigation findings, the DG may, according to the best of his judgement raise an assessment with a penalty.
v) Cases which are to be prosecuted will be forwarded to the legal department. Failure of a taxpayer to attend court proceedings after summons are served, may result in a warrant of arrest being issued |
How the CPA Group Can Help You.
Some of the ways we can help are:
- To conduct tax health checks in order to highlight potentially contentious issues
- To act as the “go-between” between the taxpayer and the IRB during the tax investigation and field audit
- To liaise and negotiate with the IRB on behalf of the taxpayer
- To provide guidance and assistance to taxpayer throughout the whole process
- To set out the options available, assess the potential tax exposures and implement a resolution plan for the taxpayer
- To provide tax litigation defense support
Offences & Penalties
| Types & Basis | Income Tax Act 1967 subsection | Penalties on Conviction | |
| (1) Failure to furnish Income Tax Return | 1 year of Assessment | 112(1) | – Fines between RM200 to RM20,000.00
– Or imprisonment not exceeding 6 months or both |
| 2 years of Assessment or more | 112(1A) | – Fines between RM1,000 to RM20,000.00
– Or imprisonment not exceeding 6 months or both – In lieu of no prosecution, pay three times the amount if tax which has been undercharged |
|
| (2) Make an incorrect tax return by omitting or understating any income
or providing incorrect information |
113(1) | – Fines between RM1,000 to RM10,000.00
– In lieu of no prosecution, pay 100% the amount of tax which has been undercharged |
|
|
(3) Willfully and intentionally evade tax or assist any other person to evade tax |
114(1) | – Fines between RM1,000 to RM20,000.00
– Or imprisonment not exceeding 3 years or both and pay special penalty of 300% of tax which has been undercharged |
|
| (4) Serious Offences
Section 112 & Section 113 of the ITA 1967 are listed as serious offences under the Anti-Money Laundering, Anti-Terrorism Financing and Proceeds of Unlawful Activities ACT 2001 (“AMLATFPUAA”). Investigation under both AMLATFPUAA and ITA may be conducted separately or concurrently. |
||
|
Types & Basis
|
AMLATFPUA
ACT 2001 Section |
Penalties on Conviction |
| Section 112 & Section 113 of the ITA 1967 | 4 | – Imprisonment not exceeding 15 years and a fine of five times or more, the sum or value of the proceeds of an unlawful activity or instrumentalities of an offence at the time the offence was committed
– or RM5 million, whichever is the higher |
| Failure to comply | 34 | – Fine not exceeding RM3 million
– Or imprisonment up to 5 years or both. |
| Continuing offence | – Fines up to RM3,000 daily during which, the offence continues after conviction. | |
Tax Appeal
- If taxpayers receive a notice of assessment and disagrees with it, they are allowed to file an appeal within 30 days of the notice to the IRBM branch which issued the assessment
- They will be required to fill up “Q Form” to appeal which is to be forwarded to the Special Commissioners of Income Tax
- If taxpayers have a valid reason to request for an extension of time (more than 30 days) to file the appeal, then they need to fill in the “N Form” to be forwarded to the Special Commissioners of Income Tax for consideration and decision.
II. Tax Compliance
Company Tax
Accordingly, companies are required to file their tax estimates 30 days before the beginning of the basis period and cannot be less than 85% of the latest estimate of the tax payable for the previous year of assessment. Two revisions of this estimate is permitted in a financial year.
Corporate tax rates in Malaysia have experienced gradual reductions since the late 1980s. The tax rate which once stood at 40% in the early years has fallen in 2020 to 24%. Furthermore, the Government provides special support to small & medium enterprises (“SMEs”).
Small & Medium Enterprise
A SME is defined as a company which has a turnover of not more than RM50 million
Corporate Income Tax Rates in Malaysia
Here are the latest tax rates as per guideline below for resident companies incorporated in Malaysia at the beginning of the basis period for Year End Assessment for 2019 and 2020 respectively.
A) For Y/A 2019, SME is defined as a company with a paid-up capital of not more than RM 2.5 million
| YEAR OF ASSESSMENT 2019 | SME | Non-SME |
| Income Tax (%) | Income Tax (%) | |
| On the first chargeable RM500,000 | 17% | 24% |
| On subsequent Chargeable Income | 24% | 24% |
B) For Y/A 2020, SME is defined as company with turnover of not more than RM50 million & a paid-up capital of not more than RM 2.5 million
| YEAR OF ASSESSMENT 2020 | SME | Non-SME |
| Income Tax (%) | Income Tax (%) | |
| On the first chargeable RM600,000 | 17% | 24% |
| On subsequent Chargeable Income | 24% | 24% |
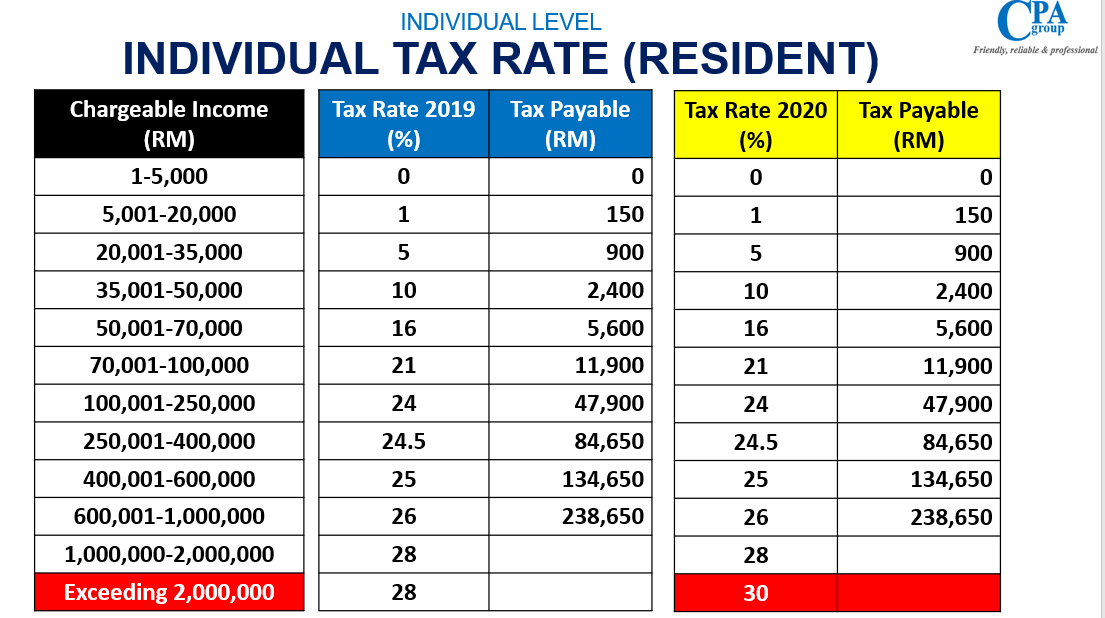
Individual Tax
The annual tax declaration by taxpayer can be done electronically by e-filing directly to the Inland Revenue or by monthly tax deduction of salary by his employer.
On the downside however, incorrect filing of the tax returns may attract tax audit on your tax account resulting into uncomfortable enquiries and the imposition of enquiries by IRB. Furthermore, there are deadlines to meet and penalties would be imposed on late submission.
Filing your tax returns, making payments and negotiating with the tax authorities need not be a hassle. Our tax professionals would be only too happy to assist you with all your corporate and personal tax needs.
Tax Year
1 January to 31 December. Income tax returns must be filed before 30 April of the following year.
Residency for Income Tax Purposes
Individuals fulfilling these criteria are liable to pay tax
(a) If the individual has been in Malaysia for 182 days in a calendar year.
(b) If an individual has been in Malaysia for less than 182 days in a calendar year, but was in the country for a total of 182 consecutive days linked to days from the year immediately preceding or following that calendar year.
(c) If an individual has been in Malaysia for at least 90 days in a calendar year and in three of the four preceding years.
(d) If an individual is resident in Malaysia in the year following and the three preceding the one being taxed.
(e) People who spend less than 182 days per year in the country are classed as non-residents and are taxed differently.
III. Other Tax Services
Other Tax Services
- Application for New Employer Tax file Number upon incorporation of a new company
- Application for New Employee Tax file Number upon incorporation of a new company
- Preparation of tax computation and timely submission of tax returns to IRB
- Preparation and submission of Form E ( Employer’s annual declaration of staff ‘s income )
- Preparation of Form EA ( Employee’s annual income statement for his / her tax filing)
3. Other Tax Information
I. Tax Incentives
Tax Incentives
Thinking about applying Tax Incentives to reduce taxable income?
Whether new set-ups, established companies, small and medium sized companies or large and multinational companies, there are numerous of tax incentives that are offered in Malaysia. They differ according to the different industries and change with the annual budget announced by the Government.
- The Malaysian Investment Authority ( MIDA ) has identified a long list of activities and manufactured products which qualifies for either tax incentives.
- This list of “promoted activities” and “promoted activities is under constant review and is updated from time to time to be in line with the latest investment policies of the government. ( Refer to MIDA’s website at http://www.mida.gov.my for a full list )
Pioneer Status & Investment Tax Allowance
- Pioneer Status (PS) – Suitable for projects with shorter gestation period & lower capital expenditure
- Investment Tax Allowance (ITA) – Suitable for projects with longer gestation period & high capital expenditure
Both are mutually exclusive; The investor can only choose to apply for either one or the other
Pioneer Status (5 to 10 Years) –
- Income Tax Exemption of 70%-100% of Statutory Income
- Exemption starts from Day 1 of Production Day ( reaches 30% of its capacity )
- Unabsorbed capital allowances and capital losses can be carried forward and deducted from the post pioneer income.
Investment Tax Allowance (5 to 10 Years) –
- 60 – 100 % Allowance on its qualifying capital expenditure (QCE) . Examples of QCE Factory, plant, machinery or other equipment use for the approved project
- Can offset ITA against 70% of Statutory Income
- Unutilised ITA can be carried forward until fully utilised
Overall Application Flow

Reinvestment Allowances













